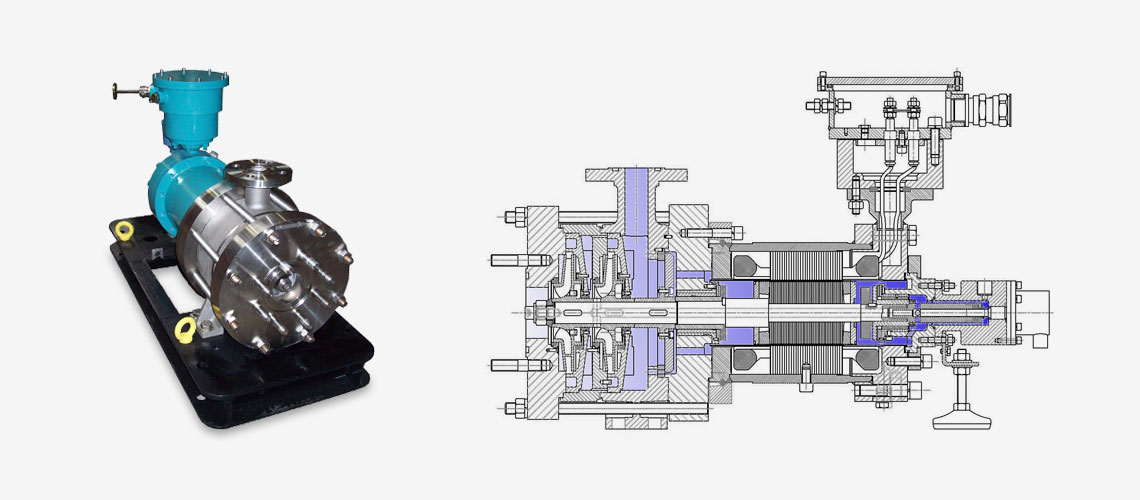
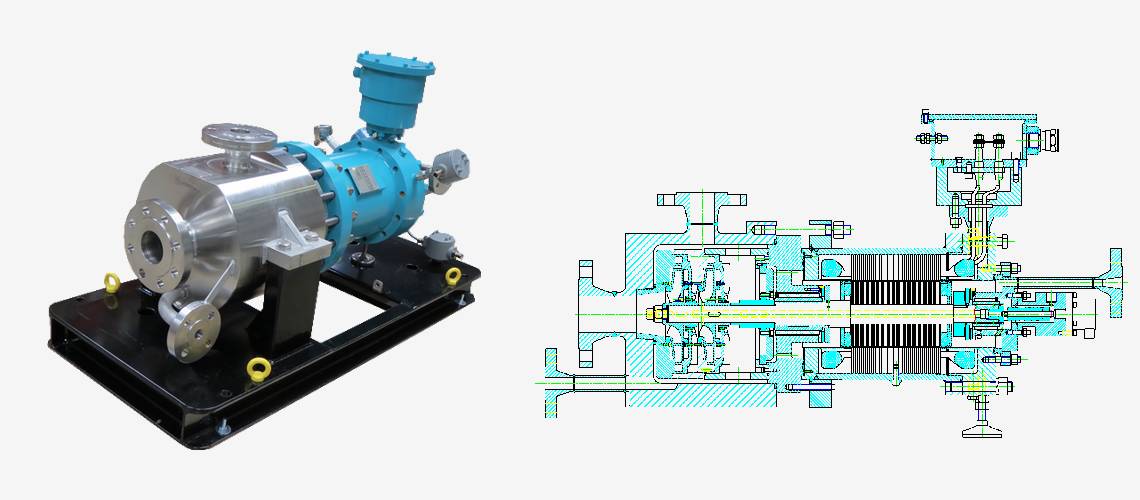
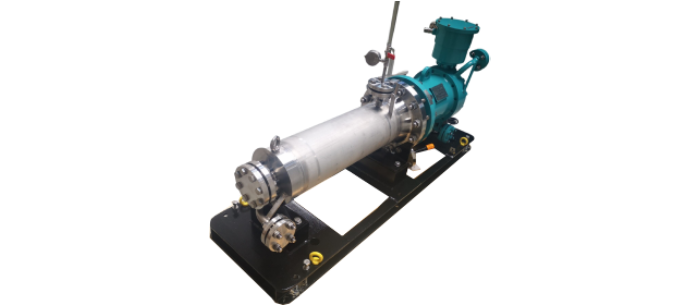
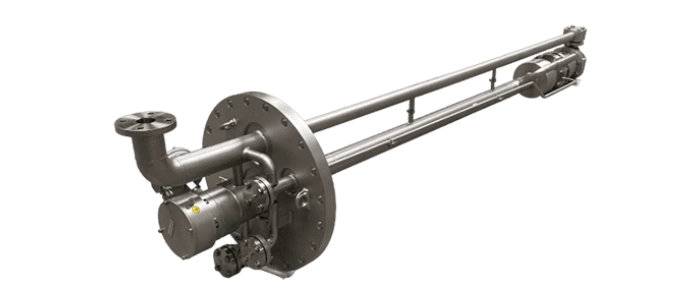
Optimex is your trusted partner for critical applications in fluid pumping, ensuring the integrity and efficiency of industrial process across various sectors. Whether it’s for transfering very dangerous fluids, extreme temperature mixture or medium with risk of solidification our canned motor pumps offer durability and reliability technical solutions.
Pumps for Chlorine
CANNED MOTOR PUMP MANUFACTURER FOR CHLORINE (CL2)
Chlorine is an essential product in the chemical industry. It has contributed to the development of several daily products that have improved our health, nutrition and quality of life. Therefore it is necessary to produce, store and transport Chlorine.
Liquid chlorine is a highly dangerous substance due to its toxic, corrosive, and reactive properties.
Examples of chlorine liquids:
- Chlorine (Cl2)
- Vynil Chloride
Pumps for Hydrofluoric Acid
CANNED MOTOR PUMPS MANUFACTURER FOR HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF)
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is an extremely dangerous and corrosive substance. Even in low concentrations, it can cause severe chemical burns that penetrate deep into tissues, affecting bones and nerves. One of the most alarming aspects of HF exposure is that the pain and damage may not be immediately apparent, which can delay treatment and increase harm. HF can also be deadly if inhaled, as it causes respiratory damage, and in severe cases, it can lead to systemic toxicity by interfering with calcium levels in the body, potentially resulting in cardiac arrest.
Despite its hazards, hydrofluoric acid has important industrial applications. It is used in glass etching, metal cleaning, and the production of fluorine-containing compounds like refrigerants and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, HF is crucial in the petrochemical industry for alkylation processes in oil refining. Due to its high risk, strict safety measures, such as specialized protective equipment and rapid medical treatment protocols, are essential when working with hydrofluoric acid.
Pumps for Phosgene
CANNED MOTOR PUMPS MANUFACTURER FOR PHOSGENE (COCL2)
Phosgene is a highly toxic and dangerous gas, primarily known for its use as a chemical weapon during World War I. Exposure to phosgene can cause severe respiratory damage. Inhalation may not immediately cause symptoms, but it can lead to delayed lung injury, including fluid buildup (pulmonary edema), which can be fatal if not treated promptly. Even brief exposure to high concentrations can result in death within hours.
Despite its hazardous nature, phosgene is still used in industry today. It is a key reagent in the production of plastics, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and dyes. It is also employed in the synthesis of isocyanates and polyurethanes. Due to its toxic effects, strict containment, safety measures, and specialized equipment are necessary when handling phosgene in industrial processes to prevent accidental exposure.